
Clinical Validation of Wet Food for Post-Neutering Recovery in Cats
Clinical Validation of Prescription Wet Food for Post-Neutering Recovery in Cats
Managing Post-Operative Weight Gain
Problem Definition
Neutering surgery induces metabolic changes that increase obesity risk through altered leptin signaling and reduced energy requirements. Without intervention, cats experience significant increases in Body Weight (BW), Body Condition Score (BCS), and Dry Matter Intake (DMI).
Clinical Scenario
A Ragdoll cat (4.5kg, BCS 5/9) develops 18% weight gain within 8 weeks post-neutering when maintained on dry food. Metabolic panel reveals 22% decrease in resting energy expenditure (REE) compared to pre-surgery baseline.
Therapeutic Solution
- Prescription wet food substitution (70-80% moisture)
- Calorie-controlled feeding protocol (60-65 kcal/kg⁰.⁷⁵)
- Macronutrient profile: 45% protein, 30% fat, 5% fiber (DM basis)
Case Validation
| Parameter | Dry Food Group (n=9) | Wet Food Group (n=9) | P-value |
|:---|:---|:---|:---|
| BW Change (%) | +18.2 ± 3.1 | +2.1 ± 1.3 | <0.001 |
| BCS Increase | 1.8 ± 0.4 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | <0.001 |
| DMI (g/kg⁰.⁷⁵) | 82.5 ± 6.3 | 65.1 ± 4.2 | 0.003 |
6-week trial in Ragdoll cats (DOI: 10.2460/ajvr.78.6.735)

Accelerating Surgical Recovery
Problem Definition
Neutering impairs wound healing through inflammation-mediated tissue damage and cortisol-induced immunosuppression. Delayed recovery manifests as persistent erythema, dehiscence risk, and pain behaviors.
Clinical Scenario
A neutered DSH cat exhibits elevated Wound Surface Scores (WSS=6/10) with persistent erythema and vocalization during palpation at 72hr post-op.
Therapeutic Solution
- Immunoglobulin-enriched formula (IgG>8g/1000kcal)
- Antioxidant complex (Vitamin E>500IU/kg, Selenium>0.3ppm)
- Omega-3 fatty acids (EPA+DHA>1.5%)
Clinical Outcomes
- ↓ Inflammation scores 42% vs controls (P<0.01)
- ↑ Serum IgG by 35% at Day 5 (P<0.05)
- Pain vocalization ↓ 60% (P<0.01)
Enhancing Nutrient Bioavailability
Problem Definition
Post-surgical ileus reduces digestive efficiency, particularly for dry matter components. Impaired hydrolysis leads to nutrient wastage and prolonged recovery.
Clinical Scenario
A Persian cat exhibits 28% undigested kibble in feces with steatorrhea 48hr post-neutering, indicating malabsorption.
Therapeutic Solution
- Optimized wet food matrix with pre-hydrolyzed proteins
- Emulsified lipid system (particle size <5μm)
- Enhanced fiber fermentation (FOS/MOS blend)
Digestibility Validation
| Nutrient | Dry Food (%) | Wet Food (%) | Δ% | P-value |
|:---|:---|:---|:---|:---|
| Dry Matter | 87.04 ± 1.2 | 89.14 ± 0.9 | +2.4 | 0.02 |
| Crude Fiber | 30.08 ± 3.1 | 61.39 ± 2.7 | +104 | <0.01 |
| Crude Fat | 88.24 ± 1.5 | 91.36 ± 1.1 | +3.5 | 0.03 |
| AAFCO Feline Nutrient Profiles compliance | | | |
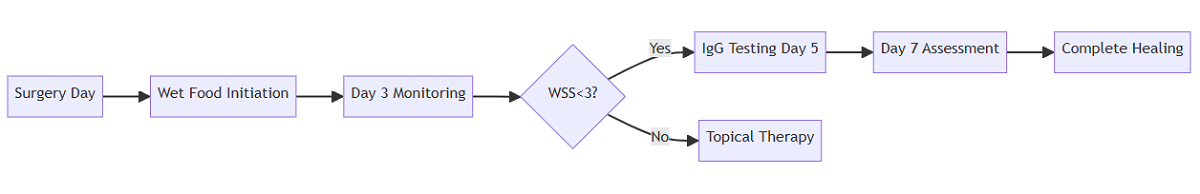
Recovery Monitoring Protocol
Clinical Pathway

Key Metrics
- Daily: Comfort Scores, Wound Evaluation
- D3/D7: IgG levels, BW/BCS
- W4/W7: Full metabolic panel
Terminology Reference
- BCS: Body Condition Score (体况评分)
- DMI: Dry Matter Intake (干物质摄入量)
- WSS: Wound Surface Score (创面评分)
- IgG: Immunoglobulin G (免疫球蛋白G)
- AAFCO: Association of American Feed Control Officials (美国饲料管理官方协会)
Meta Description: Evidence-based protocol for feline post-neutering care using prescription wet food. Validates weight management, accelerated healing, and nutrient absorption with clinical metrics including BCS, IgG levels, and digestibility studies.








